Knowledgebase
Latest from Kingshay's Knowledgebase

Kingshay grew five turnip varieties in a preferential grazing trial in the summer of 2014, to determine Which varieties gave the highest yields of dry matter, energy ...

The Sustainable Farming Incentive is one of the three parts of the new Environmental Land Management Scheme (ELMS) available to farmers in England. Key to achieving net z...

The RPA has announced six new Sustainable Farming Incentive (SFI) action offerings for 2023 (these were originally due to become available in 2024). Learnings from pilots...

Under the current Sustainable Farming Incentive (SFI 2023), 23 different options are available. With these there is more flexibility with a 'pick and mix' approach to act...

Parasites, both ectoparasites (external parasites) and endoparasites (internal parasites) can be a major cause of disease in dairy cattle. They will not only contribute t...
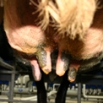
Maintaining good teat condition is a crucial line of defence against mastitis, as opportunistic pathogenic infection via the teat canal is one of the most common causes. ...
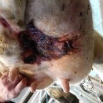
Reports of Bovine Ischemic Teat Necrosis (ITN) - which causes cattle to excessively lick and remove their teats - are on the up. The condition was first officially iden...

This year’s Kingshay Maize Variety Report emphasises the importance of choosing the right variety to reduce risk and exploit the potential of this valuable crop. Wit...

This is the fifth in a series of DAIRY insight publications covering ‘Net Zero Emissions’, where we aim to outline current and future actions that may help the UK dai...

Last published in 2017, this NEW edition of the Forage Costings Report has been fully updated to provide a detailed insight into the costs of producing forage. Using this...

This is the second issue of our new publication, RESEARCH insight. The aim of the publication is to translate relevant scientific research into useful information for you...

The future of the dairy herds on most farms, lies with their heifers. Good management from the very start is therefore key to a successful herd and is essential to reduce...
